A quick guide to WebSocket communication in Android Android 10.05.2018
WebSockets are an alternative to HTTP communication in Web Applications. They offer a long lived, bidirectional communication channel between client and server. Once established, the channel is kept open, offering a very fast connection with low latency and overhead.
HTTP is a very different protocol, and also a different way of communicate. HTTP is a request/response protocol: the server returns some data when the client requests it.
With WebSockets:
- the server can send a message to the client without the client explicitly requesting something
- the client and the server can talk to each other simultaneously
- very little data overhead needs to be exchanged to send messages. This means a low latency communication.
WebSockets are great for real-time and long-lived communications. HTTP is great for occasional data exchange and interactions initiated by the client.
Always use the secure, encrypted protocol for WebSockets, wss://. ws:// refers to the unsafe WebSockets version (the http:// of WebSockets), and should be avoided for obvious reasons.
nv-websocket-client
Let's use Tornado as Server and nv-websocket-client as WebSocket client for Android.
We are going to update the AndroidManifest.xml file by adding the following user permissions
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Add nv-websocket-client dependencies to your project dependencies by adding the following lines in your build.gradle and syncing the project:
dependencies {
...
compile 'com.neovisionaries:nv-websocket-client:2.4'
}
Following is a example of WebSocket client for Android.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
WebSocket ws = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Create a WebSocket factory and set 5000 milliseconds as a timeout
// value for socket connection.
WebSocketFactory factory = new WebSocketFactory().setConnectionTimeout(5000);
// Create a WebSocket. The timeout value set above is used.
try {
ws = factory.createSocket("ws://192.168.24.104:8888/ws/");
ws.addListener(new WebSocketAdapter() {
@Override
public void onTextMessage(WebSocket websocket, String message) throws Exception {
Log.d("TAG", "onTextMessage: " + message);
}
});
ws.connectAsynchronously();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (ws != null) {
ws.disconnect();
ws = null;
}
}
public void sendMessage(View v) {
if (ws.isOpen()) {
ws.sendText("Message from Android!");
}
}
}
Result
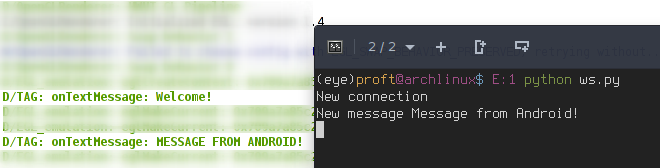
Socket.IO-client Java
Socket.IO-client Java is the Socket.IO v1.x Client Library for Java, which is simply ported from the JavaScript client.
Create server as described here.
We are going to update the AndroidManifest.xml file by adding the following user permissions
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Add socket.io-client dependencies to your project dependencies by adding the following lines in your build.gradle and syncing the project:
dependencies {
...
compile ('io.socket:socket.io-client:1.0.0') {
// excluding org.json which is provided by Android
exclude group: 'org.json', module: 'json'
}
}
Following is a example of Socket.IO client for Android.
public class CropActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Socket socket = null;
private Activity activity = CropActivity.this;
private Emitter.Listener onConnectError = new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(final Object... args) {
Log.d("TAG", "onConnectError: " + args);
}
};
private Emitter.Listener onDisconnect = new Emitter.Listener(){
@Override
public void call(final Object... args) {
if (activity != null)
activity.runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Log.d("TAG", "onDisconnect: " + args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
};
private Emitter.Listener onConnect = new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(final Object... args) {
Log.d("TAG", "onConnect: " + args);
}
};
private Emitter.Listener newMessageListner = new Emitter.Listener() {
@Override
public void call(final Object... args) {
Log.d("TAG", "newMessageListner: " + args);
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_crop);
try {
socket = IO.socket("http://192.168.24.104:8888");
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT, onConnect);
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_DISCONNECT, onDisconnect);
socket.on(Socket.EVENT_CONNECT_ERROR, onConnectError);
socket.on("newMessage", newMessageListner);
socket.connect(); //Connect socket to server
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (socket != null) {
socket.disconnect();
socket = null;
}
}
public void sendMessage(View v) {
if (socket.connected()) {
socket.emit("newMessage","Message from Android!");
}
}
}
Useful tutorials
Useful libs
- Socket class implements client sockets
- ServerSocket class implements server sockets. A server socket waits for requests to come in over the network.
- Autobahn|Java is a client library providing WAMP on Java 8 (Netty) and Android, plus (secure) WebSocket for Android.
Quote
Categories
- Android
- AngularJS
- Databases
- Development
- Django
- iOS
- Java
- JavaScript
- LaTex
- Linux
- Meteor JS
- Python
- Science
Archive ↓
- September 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- August 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013