Understanding geocoding in Android Android 03.05.2017

For this tutorial, we are going to use the Geocoder class to translate a given address into its latitude and longitude values (geocoding), and also translate a latitude and longitude value into an address (reverse geocoding).
Geocoding is the process of converting the addresses (postal address) into geo coordinates as latitude and longitude. Reverse geocoding is converting a geo coordinate latitude and longitude to an address.
The Android API contains a Geocoder class that can use either a location name or a location’s latitude and longitude values to get further details about an address (it can perform both forward and reverse geocoding). The returned address details include address name, country name, country code, postal code and more. You can read about limits here.
We need location access permission to find the latitude and longitude of the Android device. Following two lines are the key to give permission to access the location.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Geocoder has two methods for fetching an Address, getFromLocation(), which uses latitude and longitude, and getFromLocationName(), which uses the location’s name. Both methods return a list of Address objects. An Address contains information like address name, country, latitude and longitude, whereas Location contains latitude, longitude, bearing and altitude among others.
So, to achieve forward Geocode, use the below code
import android.location.Address;
import android.location.Geocoder;
...
Geocoder gc = new Geocoder(this);
List<Address> list = null;
if(gc.isPresent()) {
try {
list = gc.getFromLocationName("Karmelyuka St, 9532, Vinnytsia", 1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!list.isEmpty()) {
Address address = list.get(0);
double lat = address.getLatitude();
double lng = address.getLongitude();
Log.d(TAG, "Lat: " + String.valueOf(lat) + ", Lng: " + String.valueOf(lng));
}
}
To achieve reverse Geocode, use the below code
Geocoder gc = new Geocoder(context);
List<Address> list = null;
if(gc.isPresent()) {
try {
list = gc.getFromLocation(49.2327, 28.4856, 1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!list.isEmpty()) {
Address address = list.get(0);
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
str.append("Name: " + address.getLocality() + "\n");
str.append("Sub-Admin Ares: " + address.getSubAdminArea() + "\n");
str.append("Admin Area: " + address.getAdminArea() + "\n");
str.append("Country: " + address.getCountryName() + "\n");
str.append("Country Code: " + address.getCountryCode() + "\n");
String strAddress = str.toString();
Log.d(TAG, strAddress);
}
}
Let's develop simple app that will do forward or reverse geocoding in background using IntentService.
Our app is going to use both forward and reverse geocoding to get location address, and the app layout reflects this. The layout contains two EditTexts for latitude and longitude respectively, and an EditText for address name input. Beneath these, we have two RadioButtons, to select if we are fetching an address using the location’s latitude/longitude values, or using the address name. There is a Button, that begins the geocoding lookup when clicked, a ProgressBar, to show the user that the lookup task is running in the background, and a TextView to show the result received.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:orientation="vertical">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etLatitude"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Latitude"
android:inputType="numberDecimal|numberSigned"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etLongitude"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/etLatitude"
android:hint="Longitude"
android:inputType="numberDecimal|numberSigned"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etAddress"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/etLongitude"
android:minLines="4"
android:hint="Address"
android:scrollHorizontally="false"
android:scrollbars="vertical"
android:enabled="false"/>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/rgSwitchers"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/etAddress"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rbLocation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Use location"
android:checked="true"
android:onClick="onRadioButtonClicked"/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rbAddress"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Use address"
android:onClick="onRadioButtonClicked"/>
</RadioGroup>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnGet"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/rgSwitchers"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="Get"
android:onClick="onButtonClicked"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvInfo"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/btnGet"/>
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pbResult"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tvInfo"
android:visibility="invisible"/>
</RelativeLayout>
To perform a long running task in the background, we can use an AsyncTask. However, the AsyncTask is not recommended for operations like the Geocoder lookup, because it can take a potentially long time to return. AsyncTask's should be used for comparatively shorter operations. We would use an IntentService. An IntentService extends Service, and operations run in it can take as long as necessary. An IntentService holds no reference to the Activity it was started from, and so, the activity can be rebuilt (like when the device is rotated), without affecting the IntentService’s tasks, unlike the AsyncTask.
We extend IntentService and define GeocodeIntentService. An IntentService is started much like an Activity. We build an Intent, and start the service by calling Context.startService() method.
Before defining the class, we include our GeocodeIntentService in the AppManifest.
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="me.proft.geocoding">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<application
...
<service
android:name=".GeocodeIntentService"
android:exported="false"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Next step is to define Constants class with constants.
public final class Constants {
public static final String FETCH_TYPE_EXTRA = "FETCH_TYPE_EXTRA";
public static final String LOCATION_NAME_DATA_EXTRA = "LOCATION_NAME_DATA_EXTRA";
public static final String RECEIVER = "RECEIVER";
public static final String RESULT_DATA_KEY = "RESULT_DATA_KEY";
public static final String RESULT_ADDRESS = "RESULT_ADDRESS";
public static final String LOCATION_LATITUDE_DATA_EXTRA = "LOCATION_LATITUDE_DATA_EXTRA";
public static final String LOCATION_LONGITUDE_DATA_EXTRA = "LOCATION_LONGITUDE_DATA_EXTRA";
public static final int SUCCESS_RESULT = 0;
public static final int FAILURE_RESULT = 1;
public static final int USE_ADDRESS_NAME = 1;
public static final int USE_ADDRESS_LOCATION = 2;
}
The code snippet below contains the actual forward or reverse geocoding lookup calls. We determine if the search uses location name, or location latitude/longitude values, and call the appropriate method. If using location name, we call the Geocoder.getFromLocationName() method, and if using latitude/longitude, we call Geocoder.getFromLocation() method. You can specify a maximum number of addresses to be returned. In our sample, we request for a maximum of one (1) address. Note that an address name can refer to more than one location, spread across multiple countries. In a production app, you might want to fetch more than one, and have an algorithm determine which is the most likely required address.
To use our IntentService, we must implement the onHandleIntent(Intent) method. This is the entry point for IntentService’s, much like the onCreate() is the entry point for Activity’s. In the code snippet below, take notice of the ResultReceiver object. When your IntentService has completed it’s task, it should have a way to send the results back to the invoking Activity. That is where the ResultReceiver comes in.
deliverResultToReceiver is a simple method, that handles returning the results of the operation to the invoking Activity, through the ResultReceiver.
import android.location.Address;
import android.location.Geocoder;
...
public class GeocodeIntentService extends IntentService {
protected ResultReceiver resultReceiver;
private static final String TAG = "GEO";
public GeocodeIntentService() {
super("GeocodeIntentService");
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Geocoder geocoder = new Geocoder(this, Locale.getDefault());
String errorMessage = "";
List<Address> addresses = null;
int fetchType = intent.getIntExtra(Constants.FETCH_TYPE_EXTRA, 0);
if(fetchType == Constants.USE_ADDRESS_NAME) {
String name = intent.getStringExtra(Constants.LOCATION_NAME_DATA_EXTRA);
try {
addresses = geocoder.getFromLocationName(name, 1);
} catch (IOException e) {
errorMessage = "Service not available";
Log.e(TAG, errorMessage, e);
}
}
else if(fetchType == Constants.USE_ADDRESS_LOCATION) {
double latitude = intent.getDoubleExtra(Constants.LOCATION_LATITUDE_DATA_EXTRA, 0);
double longitude = intent.getDoubleExtra(Constants.LOCATION_LONGITUDE_DATA_EXTRA, 0);
try {
addresses = geocoder.getFromLocation(latitude, longitude, 1);
} catch (IOException ioException) {
errorMessage = "Service Not Available";
Log.e(TAG, errorMessage, ioException);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException illegalArgumentException) {
errorMessage = "Invalid Latitude or Longitude Used";
Log.e(TAG, errorMessage + ". " +
"Latitude = " + latitude + ", Longitude = " +
longitude, illegalArgumentException);
}
}
else {
errorMessage = "Unknown Type";
Log.e(TAG, errorMessage);
}
resultReceiver = intent.getParcelableExtra(Constants.RECEIVER);
if (addresses == null || addresses.size() == 0) {
if (errorMessage.isEmpty()) {
errorMessage = "Not Found";
Log.e(TAG, errorMessage);
}
deliverResultToReceiver(Constants.FAILURE_RESULT, errorMessage, null);
} else {
for(Address address : addresses) {
String outputAddress = "";
for(int i = 0; i < address.getMaxAddressLineIndex(); i++) {
outputAddress += " --- " + address.getAddressLine(i);
}
Log.e(TAG, outputAddress);
}
Address address = addresses.get(0);
ArrayList<String> addressFragments = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < address.getMaxAddressLineIndex(); i++) {
addressFragments.add(address.getAddressLine(i));
}
String addressResult = TextUtils.join(System.getProperty("line.separator"), addressFragments);
deliverResultToReceiver(Constants.SUCCESS_RESULT, addressResult, address);
}
}
private void deliverResultToReceiver(int resultCode, String message, Address address) {
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable(Constants.RESULT_ADDRESS, address);
bundle.putString(Constants.RESULT_DATA_KEY, message);
resultReceiver.send(resultCode, bundle);
}
}
And MainActivity.java file.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
AddressResultReceiver resultReceiver;
EditText etLatitude, etLongitude, etAddress;
ProgressBar pbResult;
TextView tvInfo;
boolean fetchAddress;
int fetchType = Constants.USE_ADDRESS_LOCATION;
private static final String TAG = "GEO";
public class AddressResultReceiver extends ResultReceiver {
public AddressResultReceiver(Handler handler) {
super(handler);
}
@Override
protected void onReceiveResult(int resultCode, final Bundle resultData) {
if (resultCode == Constants.SUCCESS_RESULT) {
final Address address = resultData.getParcelable(Constants.RESULT_ADDRESS);
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pbResult.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
tvInfo.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
tvInfo.setText("Latitude: " + address.getLatitude() + "\n" +
"Longitude: " + address.getLongitude() + "\n" +
"Address: " + resultData.getString(Constants.RESULT_DATA_KEY));
}
});
} else {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pbResult.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
tvInfo.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
tvInfo.setText(resultData.getString(Constants.RESULT_DATA_KEY));
}
});
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
etLongitude = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.etLongitude);
etLatitude = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.etLatitude);
etAddress = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.etAddress);
pbResult = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.pbResult);
tvInfo = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvInfo);
resultReceiver = new AddressResultReceiver(null);
}
public void onRadioButtonClicked(View view) {
boolean checked = ((RadioButton) view).isChecked();
switch(view.getId()) {
case R.id.rbAddress:
if (checked) {
fetchAddress = false;
fetchType = Constants.USE_ADDRESS_NAME;
etLongitude.setEnabled(false);
etLatitude.setEnabled(false);
etAddress.setEnabled(true);
etAddress.requestFocus();
}
break;
case R.id.rbLocation:
if (checked) {
fetchAddress = true;
fetchType = Constants.USE_ADDRESS_LOCATION;
etLatitude.setEnabled(true);
etLatitude.requestFocus();
etLongitude.setEnabled(true);
etAddress.setEnabled(false);
}
break;
}
}
public void onButtonClicked(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, GeocodeIntentService.class);
intent.putExtra(Constants.RECEIVER, resultReceiver);
intent.putExtra(Constants.FETCH_TYPE_EXTRA, fetchType);
if(fetchType == Constants.USE_ADDRESS_NAME) {
if(etAddress.getText().length() == 0) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter address", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
intent.putExtra(Constants.LOCATION_NAME_DATA_EXTRA, etAddress.getText().toString());
}
else {
if(etLatitude.getText().length() == 0 || etLongitude.getText().length() == 0) {
Toast.makeText(this,
"Please enter latitude and longitude",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
intent.putExtra(Constants.LOCATION_LATITUDE_DATA_EXTRA,
Double.parseDouble(etLatitude.getText().toString()));
intent.putExtra(Constants.LOCATION_LONGITUDE_DATA_EXTRA,
Double.parseDouble(etLongitude.getText().toString()));
}
tvInfo.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
pbResult.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
Log.e(TAG, "Starting Service");
startService(intent);
}
}
Starting the IntentService is pretty similar to starting a new Activity. We build an Intent, put in the necessary Extras, and call Context.startService(Intent). The Extras we bundle in the Intent is dependent on if we are performing a forward or reverse lookup.
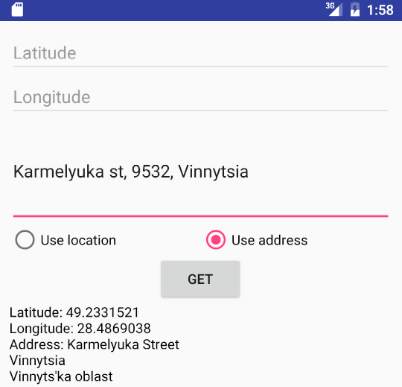
Result
Quote
Categories
- Android
- AngularJS
- Databases
- Development
- Django
- iOS
- Java
- JavaScript
- LaTex
- Linux
- Meteor JS
- Python
- Science
Archive ↓
- September 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- August 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013