How to simplify SQLite operations by GreenDAO ORM Android 09.03.2017
There are several ways to persist data on Android
In this tutorial you will learn how to use SQLite database easier and simplifying the database-related boilerplate code to a minimum and abstracting the relational database operations with GreenDAO.
GreenDAO is an object/relational mapping (ORM) tool for Android. To start using it in your project, all you have to do is to define your data model. GreenDAO then generates all the DAOs (Data Access Object) and database helper classes automatically for you.
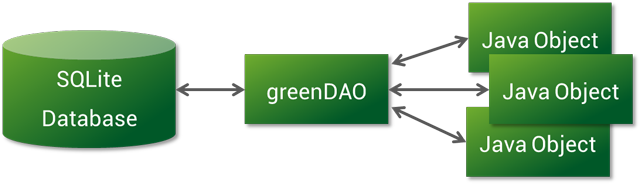
You don’t actually need to bother how to populate the database and how the relations work, because GreenDAO handles it for you. All you need to know is what you want to keep in your DB.
GreenDAO is one of the many existing Android ORM database libraries. The main advantage of GreenDAO over other Android ORM database libraries, is its high performance. According to their report, GreenDAO outperforms all the other compared ORM libraries.
GreenDAO's features at a glance
- Maximum performance (probably the fastest ORM for Android).
- Easy to use powerful APIs covering relations and joins.
- Minimal memory consumption.
- Small library size (<100KB) to keep your build times low and to avoid the 65k method limit.
- Database encryption: GreenDAO supports SQLCipher to keep your user’s data safe.
- Strong community: More than 5.000 GitHub stars show there is a strong and active community.
In order to use GreenDAO in your Android project, you need to add the GreenDAO Gradle plugin and add the GreenDAO library.
Add following snippet to Gradle project
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.greenrobot:greendao-gradle-plugin:3.2.1'
}
}
Add following snippet to Gradle module
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'org.greenrobot.greendao'
android {
...
}
greendao {
schemaVersion 1
}
dependencies {
compile 'org.greenrobot:greendao:3.2.0'
}
The following core classes are the essential interface to GreenDAO
- DaoMaster. The entry point for using GreenDAO.
DaoMasterholds the database object (SQLiteDatabase) and manages DAO classes (not objects) for a specific schema. It has static methods to create the tables or drop them. Its inner classesOpenHelperandDevOpenHelperareSQLiteOpenHelperimplementations that create the schema in the SQLite database. - DaoSession. Manages all available DAO objects for a specific schema, which you can acquire using one of the getter methods.
DaoSessionprovides also some generic persistence methods like insert, load, update, refresh and delete for entities. Lastly, aDaoSessionobjects also keeps track of an identity scope. For more details, have a look at the session documentation. - DAOs. Data access objects (DAOs) persists and queries for entities. For each entity, GreenDAO generates a DAO. It has more persistence methods than
DaoSession, for example:count,loadAll, andinsertInTx. - Entities. Persistable objects. Usually, entities are objects representing a database row using standard Java properties (like a POJO or a JavaBean).
Let’s have a look now on how to create a model class (Entities) to be used with GreenDAO. In our example, we want to store information about movies such as their title, their year of release and a list of their actors. Therefore, we create two data model classes: Movie and Actor. Each class has to be annotated by the @Entity annotation for GreenDAO to recognize it.
File Movie.java
@Entity
public class Movie {
@Id
private Long id;
@NotNull
private String title;
@Transient
private int year;
@ToMany(referencedJoinProperty = "movieId")
private List<Actor> actors;
}
File Actor.java
@Entity
public class Actor {
@Id
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
@NotNull
@Index(name = "AGE_IDX")
private int age;
@NotNull
private Long movieId;
}
To explain some of the annotations used
@Idselects along/Longproperty as the entity ID and a primary key.@Propertyallows to redefine the default column name for the property (by default it is transformed e.g. fromyearOfReleasetoYEAR_OF_RELEASE).@NotNulladds aNOT NULLconstrain to the database column (useful for primitive data types).@Transientmarks the property to be excluded from the database (e.g. for temporary data).@Indexcreate an index on the property.
To define relations between tables/model classes, annotations @ToOne and @ToMany can be used. You just need to specify the joinProperty or referencedJoinProperty respectively.
In order to be able to work with the database objects, the datamodel module has to be compiled first. Press Ctrl + F9 or select Build > Make Project. By doing that, all the DAO classes and helper classes get created.
Let's initialize DaoMaster and DaoSession as singleton.
public class MyApplication extends Application {
private DaoSession daoSession;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper helper = new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this, "movies");
Database db = helper.getWritableDb();
daoSession = new DaoMaster(db).newSession();
}
public DaoSession getDaoSession() {
return daoSession;
}
}
And add correct application tag in AndroidManifest.xml
<application
android:name=".MyApplication"
...
After that, operations of inser, list, delete into the database is very simple:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
long movieNum = 0, actorNum = 0;
DaoSession daoSession;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
daoSession = ((MyApplication)getApplication()).getDaoSession();
}
public void createMovie(View v) {
// create Movie object
movieNum += 1;
Movie movie1 = new Movie(null, "Movie" + String.valueOf(movieNum));
long movieID = daoSession.getMovieDao().insert(movie1);
// create Actor objects
List<Actor> actors = new ArrayList<>(2);
actorNum += 1;
Actor actor1 = new Actor(null, "Name " + String.valueOf(actorNum),
"LastName " + String.valueOf(actorNum), 24, movieID);
actors.add(actor1);
actorNum += 1;
Actor actor2 = new Actor(null, "Name " + String.valueOf(actorNum),
"LastName " + String.valueOf(actorNum), 24, movieID);
actors.add(actor2);
// add actors to movie
daoSession.getActorDao().insertInTx(actors);
}
public void listMovies(View v) {
List<Movie> movies = daoSession.getMovieDao().loadAll();
List<String> actorsList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Movie m : movies) {
for (Actor a : m.getActors()) {
actorsList.add(a.getFirstName() + " " + a.getLastName());
}
String actors = TextUtils.join(", ", actorsList);
actorsList.clear();
Log.d("TAG", String.format("%s (%s)", m.getTitle(), actors));
}
}
public void deleteMovies(View v) {
daoSession.getMovieDao().deleteAll();
daoSession.getActorDao().deleteAll();
}
}
Querying the database is made simple with the QueryBuilder. An example shows creating a query using join for get only Movie objects with Actor with age bigger than 20.
QueryBuilder<Movie> queryBuilder = daoSession.getMovieDao().queryBuilder();
queryBuilder.join(Actor.class, ActorDao.Properties.MovieId)
.where(ActorDao.Properties.Age.ge(20));
List<Movie> joined = queryBuilder.list();
An example shows how to select Movie object and update value
Movie movie = daoSession.getMovieDao()
.queryBuilder().where(MovieDao.Properties.Title.eq("Movie 1"));
movie.setTitle("The Shawshank Redemption");
movie.update();
An example shows how to delete Movie object and related Actor
daoSession.getActorDao().deleteInTx(movie.getActors()); movie.delete();
How to view and edit SQLite database from browser
For this task we'll use Android-Debug-Database. Android Debug Database is a powerful library for debugging databases and shared preferences in Android applications.
What can Android Debug Database do?
- See all the databases.
- See all the data in the shared preferences used in your application.
- Run any sql query on the given database to update and delete your data.
- Directly edit the database values.
- Directly edit shared preferences.
- Delete database rows and shared preferences.
- Search in your data.
- Sort data.
- Download database.
Add this to your app's build.gradle.
debugCompile 'com.amitshekhar.android:debug-db:1.0.0'
Use debugCompile so that it will only compile in your debug build and not in your release apk.
That's all, just start the application, you will see in the logcat an entry like follows :
- D/DebugDB: open http://XXX.XXX.X.XXX:8080 in your browser
- You can also always get the debug address url from your code by calling the method
DebugDB.getAddressLog();
To view data from Android Default Emulator run following commands from terminal
# list devices adb devices # forward port adb -s emulator-5554 forward tcp:8080 tcp:8080 # open in browser chromium http://localhost:8080
Quote
Categories
- Android
- AngularJS
- Databases
- Development
- Django
- iOS
- Java
- JavaScript
- LaTex
- Linux
- Meteor JS
- Python
- Science
Archive ↓
- September 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- August 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013