Implementing Paging Library in Android Android 25.05.2020
The Paging library is another library added to the Architecture Components. The library helps efficiently manage the loading and display of a large data set in the RecyclerView. Android paging library makes it easy to load data gradually and gracefully within our app’s RecyclerView.
Advantages of Paging Library
- Paging library data request consumes less network bandwidth and fewer system resources. So the user needed a small data plan will appreciate a data conscious app .
- App gives quick response even during the data update and refresh and also continue to respond quickly to the user input.
To use paging you have to know about it members:
PagedList. APagedListis a special kind ofListfor showing paged data in Android. PagedList object is passed to RecyclerView by creating LiveData of pages.DataSource(and Data Source Factory) + Repository. DataSource is used for loading data by PagedList. You can create DataSource by extending one of the three data source classes such asPageKeyedDataSource,ItemKeyedDataSource, orPositionalDataSource. You need to implementloadInitialandloadAftermethods. Using parameters inloadInitialandloadAftermethods, you can prepare query and load data.- RecyclerView + DiffUtil + PagedListAdapter (inherit from the ListAdapter class instead of the RecyclerView.Adapter).
PagedListAdaptercallsloadAroundonPagedListobject to makePagedListload data for next pages as user scrolls the items in recycler view.PagedListAdapterlistens for data changes and displays the changes in recycler view.
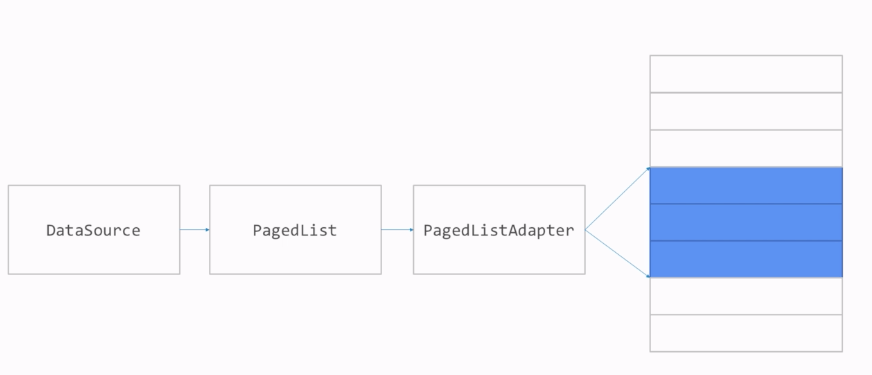
Pagination library needs DataSource to give us what we need. DataSource is the class where you tell your application about how much data you want to load in your application. There’re three choices ItemKeyedDataSource, PageKeyedDataSource and PositionalDataSource.
- Use
PageKeyedDataSourceif your feeds page has some feature of next or previous post. For example, you can see the next post by clicking the next button in any social media platform. - Use
ItemKeyedDataSourceif you want the data of an item with the help of the previous item. For example, while commenting to a post, you need the id of the last comment to get the content of the next comment. - Use
PositionalDataSourceif you want to fetch data only from a specific location then you can usePositionalDataSource. For example, out of 1000 users, if you want to fetch the data of the users from 300 to 400 then you can do this by usingPositionalDataSource.
Implementation
First, let’s add the Pagination library to our project. I’ve used version 2.1.1:
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:${paging}"
In following example we'll load data from Firestore and show in PagedListAdapter.
Let’s create a model class
data class Movie(val title: String, val year: Int)
Create a Data Source
The Paging Library requires that the data used in the RecyclerView, regardless of whether they are pulled from the network, database, or memory, be defined as data sources.
In data source, we have to override 3 methods.
loadInitialloads the first page of your data that use to initialize RecyclerViewloadBeforeused when to scroll uploadAfterused when to scroll down
class MoviesDataSource: ItemKeyedDataSource<Movie, Movie>() {
val rep = MovieRepository()
override fun loadInitial(params: LoadInitialParams<Movie>, callback: LoadInitialCallback<Movie>) {
rep.getMovies(null, params.requestedLoadSize, callback)
}
override fun loadAfter(params: LoadParams<Movie>, callback: LoadCallback<Movie>) {
rep.getMovies(params.key, params.requestedLoadSize, callback)
}
override fun loadBefore(params: LoadParams<Movie>, callback: LoadCallback<Movie>) {}
override fun getKey(item: Movie): Movie {
return item
}
}
class MovieRepository {
val db = FirebaseFirestore.getInstance()
fun getMovies(movie: Movie?, size: Int, callback: ItemKeyedDataSource.LoadCallback<Movie>) {
val query = db.collection("databases/movies").orderBy("title", Query.Direction.DESCENDING);
movie?.let {
query.startAfter(movie)
}
query.limit(size.toLong()).get().addOnSuccessListener {
if (it != null) {
val items = it.toObjects(Movie::class.java)
if (items.isEmpty()) return@addOnSuccessListener
callback.onResult(items)
}
}
}
}
Using Data Source we need DataSource.Factory which extends DataSource.Factory. Basically it just a factory for DataSources.
val dataSourceFactory = object : DataSource.Factory<Movie, Movie>() {
override fun create(): DataSource<Movie, Movie> {
return MoviesDataSource()
}
}
Create a PageList
A PageList takes in 4 important parameters:
setEnablePlaceholders. Enabling placeholders mean there is a placeholder that is visible to the user till the data is fully loaded. So for instance, if we have 20 items that are needed to be loaded and each item contains an image, when we scroll through the screen, we can see placeholders instead of the image since it is not fully loaded.setInitialLoadSizeHint. The number of items to load initially.setPageSize(). The number of items to load in the PagedList.setPrefetchDistance. The number of preloads that occur. For instance, if we set this to 10, it will fetch the first 10 pages initially when the screen loads.
val config = PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.setPrefetchDistance(6)
.setPageSize(12)
.build()
Set up PagedListAdapter
Now we have data ready to load in page by page fashion. We need to create an adapter that accepts this data.
class MoviePagedAdapter : PagedListAdapter<Movie, MoviePagedAdapter.ViewHolder>(COMPARATOR) {
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): MoviePagedAdapter.ViewHolder {
val view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.context).inflate(R.layout.movie_item, parent, false)
return ViewHolder(view)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: MoviePagedAdapter.ViewHolder, position: Int) {
val movie = getItem(position)
movie?.let {
holder.bindTo(movie)
}
}
class ViewHolder(itemView: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(itemView) {
fun bindTo(item: Movie) {
with(itemView) {
tvName.setText(item.title);
}
}
}
companion object {
private val COMPARATOR = object : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Movie>() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: Movie, newItem: Movie): Boolean =
oldItem.userId == newItem.userId
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: Movie, newItem: Movie): Boolean =
oldItem == newItem
}
}
}
Gather all components in MainActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
val movieAdapter = MoviePagedAdapter()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val dataSourceFactory = object : DataSource.Factory<Movie, Movie>() {
override fun create(): DataSource<Movie, Movie> {
return MoviesDataSource()
}
}
val config = PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.setPrefetchDistance(6)
.setPageSize(12)
.build()
val pagedListLiveData = LivePagedListBuilder(dataSourceFactory, config).build()
pagedListLiveData.observe(this, Observer {
movieAdapter.submitList(it)
})
rvItems.adapter = movieAdapter
rvItems.layoutManager = GridLayoutManager(this, 2)
}
}
Useful links
Quote
Categories
- Android
- AngularJS
- Databases
- Development
- Django
- iOS
- Java
- JavaScript
- LaTex
- Linux
- Meteor JS
- Python
- Science
Archive ↓
- September 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- August 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013