Example of ListFragment in Android Android 12.05.2014
Fragment class in Android is used to simplifies the task of creating UI for multiple screen sizes. Fragments should be used within the Activity, last can contain any number of fragments.
Let's initialize a string constant inside string.xml file under res/values directory
<resources>
...
<string-array name="planets">
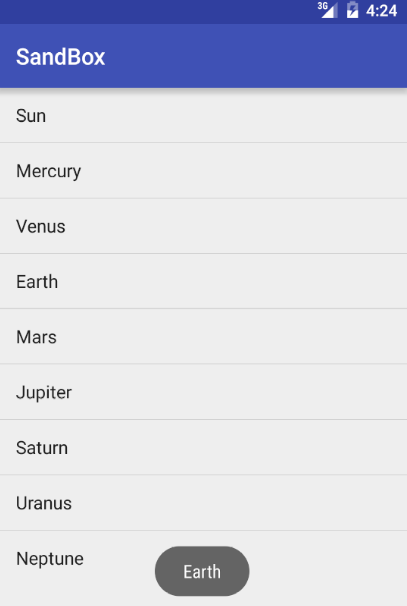
<item>Sun</item>
<item>Mercury</item>
<item>Venus</item>
<item>Earth</item>
<item>Mars</item>
<item>Jupiter</item>
<item>Saturn</item>
<item>Uranus</item>
<item>Neptune</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
Creating Fragment layouts in list_fragment.xml file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ListView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@android:id/list" />
</LinearLayout>
Create a class PlanetListFragment and extend it to ListFragment. Inside the onCreateView() method, inflate the view with above defined list_fragment.xml layout. Inside the onActivityCreated() method, create a ArrayAdapter from resource array R.array.planets and set this adapter to ListView and also set the onItemClick click listener. Inside the OnItemClickListener() method, display a toast message with item name which is being clicked.
public class PlanetListFragment extends ListFragment implements AdapterView.OnItemClickListener {
ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_planet_list, container, false);
return view;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(getActivity(), R.array.planets, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
setListAdapter(adapter);
getListView().setOnItemClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), adapter.getItem(position), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
What exactly is an adapter? An adapter loads the information to be displayed from a data source, such as an array or database query and creates a view for each item. Then it inserts the views into the ListView. The adapter acts as the middle man between the ListView and data source, or its provider. It works kind of like this: the ListView asks the adapter what it should display, and the adapter jumps into action:
- It fetches the items to be displayed from the data source.
- It decides how they should be displayed.
- It passes this information on to the
ListView.
Our main layout (activity_main.xml) consists of one fragment which are displayed vertically. Fragment should link to the fragment class which is defined.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context="me.proft.sandbox.MainActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
class="me.proft.sandbox.PlanetListFragment"/>
</LinearLayout>
Our MainActivity just extends the FragmentActivity.
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
Result
Quote
Categories
- Android
- AngularJS
- Databases
- Development
- Django
- iOS
- Java
- JavaScript
- LaTex
- Linux
- Meteor JS
- Python
- Science
Archive ↓
- September 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- August 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013