Celery for periodic tasks in Django projects Django 25.10.2013
Celery is useful for background task processing and deferred execution in Django. Task queues are used to distribute work across workers.
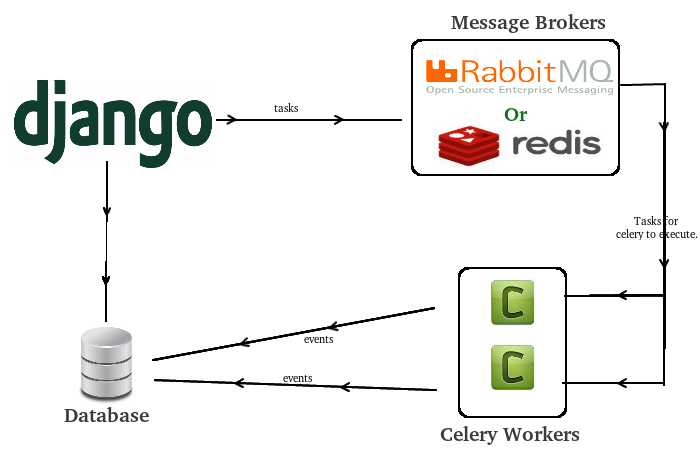
Celery's components
- message broker - component for exchange messages and tasks distribution between workers, popular implementation are RabbitMQ and Redis;
- worker - calculation unit, which execute task;
- application - application that requires background task processing or deferred execution;
- task - unit for anisochronous execution;
- result backends (result storage) - place where we can store results after deferred execution or background task processing, popular implementation are SQLAlchemy/Django ORM, Memcached, Redis, AMQP (RabbitMQ), and MongoDB;
Input for celery is message broker, output is result backends (if required).
Redis as broker and result storage
Redis with Celery is useful for simple tasks that can allocated at RAM.
Install redis
# archlinux yaourt -S redis # ubuntu sudo apt-get install redis-server
Install django-celery-with-redis
pip install django-celery-with-redis
Add djcelery to INSTALLED_APPS (to settings.py).
Setup message broker and result backends (in settings.py).
# vim project/settings.py
import djcelery
djcelery.setup_loader()
# format is redis://:password@hostname:port/db_number
BROKER_URL = 'redis://localhost:6379/0'
CELERY_RESULT_BACKEND = 'redis://localhost:6379/0'
REDIS_CONNECT_RETRY = True
# how long store results (in this case 5 hours)
CELERY_TASK_RESULT_EXPIRES = 18000
CELERY_TIMEZONE = 'UTC'
# send errors to admin (emails from settings.ADMINS)
CELERND_TASK_ERROR_EMAILS = True
# periodic tasks
CELERYBEAT_SCHEDULE = {
# feed animal every 24h
'update-web-sites': {
'task': 'animals.tasks.feed_all_cats',
'schedule': crontab(minute=0, hour=0),
}
}
Update database
# if south python manage.py migrate djcelery # else python manage.py syncdb
Power up worker
python manage.py celery worker -l info
I am going to setup test application - animals. In this application I'll create file tasks.py and declare two simple tasks.
# vim animals/tasks.py
from celery.task import task
from animals.models import Animal
from random import randint
from celery.schedules import crontab
from celery.decorators import periodic_task
@task
def new_animal_task(num):
Animal.objects.create(title="Animal %s" % num)
return True
@periodic_task(run_every=crontab(minute='*/1'))
def new_animal_task_every_minute():
Animal.objects.create(title="Animal %s" % randint(1, 1000))
return True
Let's start django shell and test our task
# python manage.py shell from animals.tasks import new_animal_task from random import randint num = randint(1, 1000) result = new_animal_task.delay(num) result.task_id # check out the status of task result.status 'SUCCESS' # get result result.result
Monitoring
List active nodes in this cluster
python manage.py celery status
List active tasks
python manage.py celery inspect active
Show worker statistics
python manage.py celery inspect stats
celery events is a simple curses monitor displaying task and worker history. You can inspect the result and traceback of tasks, and it also supports some management commands like rate limiting and shutting down workers.
python manage.py celery events
More about monitoring.
Run workers from supervisord
More about supervisord (on russian).
Let's declare worker's runer for supervisor.
# sudo vim /etc/supervisord.conf ;======================================= ; celeryd supervisord script for django ; ======================================= [program:celery] command=/path/to/project/manage.py celery worker -B -E --loglevel=INFO directory=/path/to/project user=nobody numprocs=1 stdout_logfile=/var/log/project/celeryd.log stderr_logfile=/var/log/project/celeryd.log autostart=true autorestart=true startsecs=10 stopwaitsecs=30
Useful links
Quote
Categories
- Android
- AngularJS
- Databases
- Development
- Django
- iOS
- Java
- JavaScript
- LaTex
- Linux
- Meteor JS
- Python
- Science
Archive ↓
- September 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- August 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013